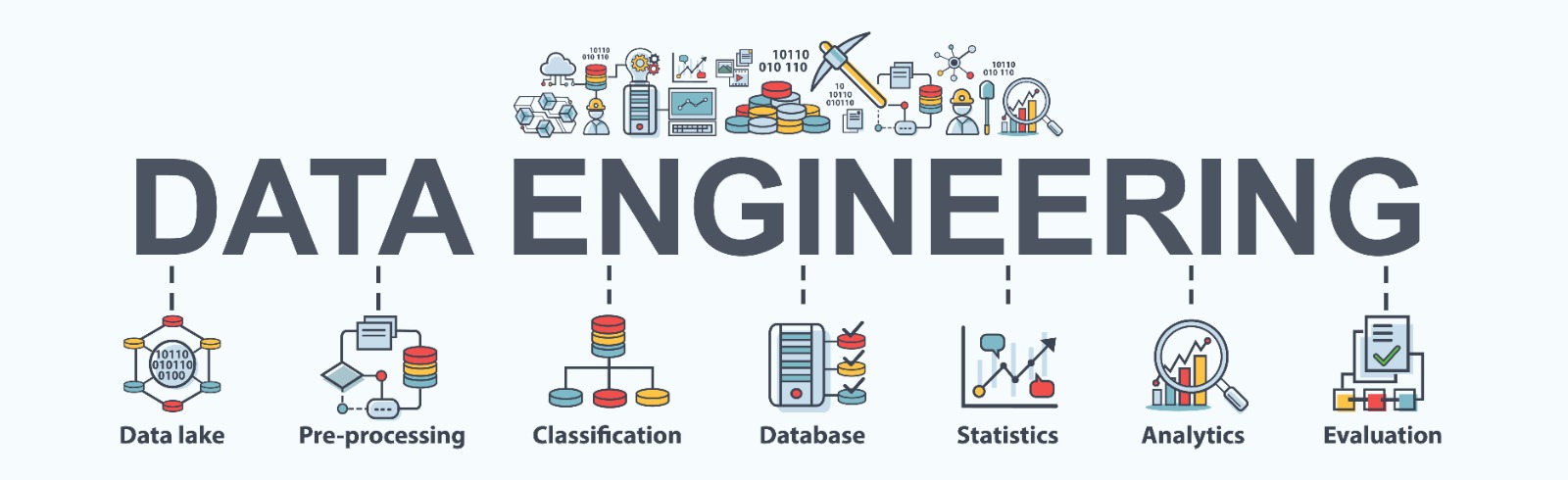
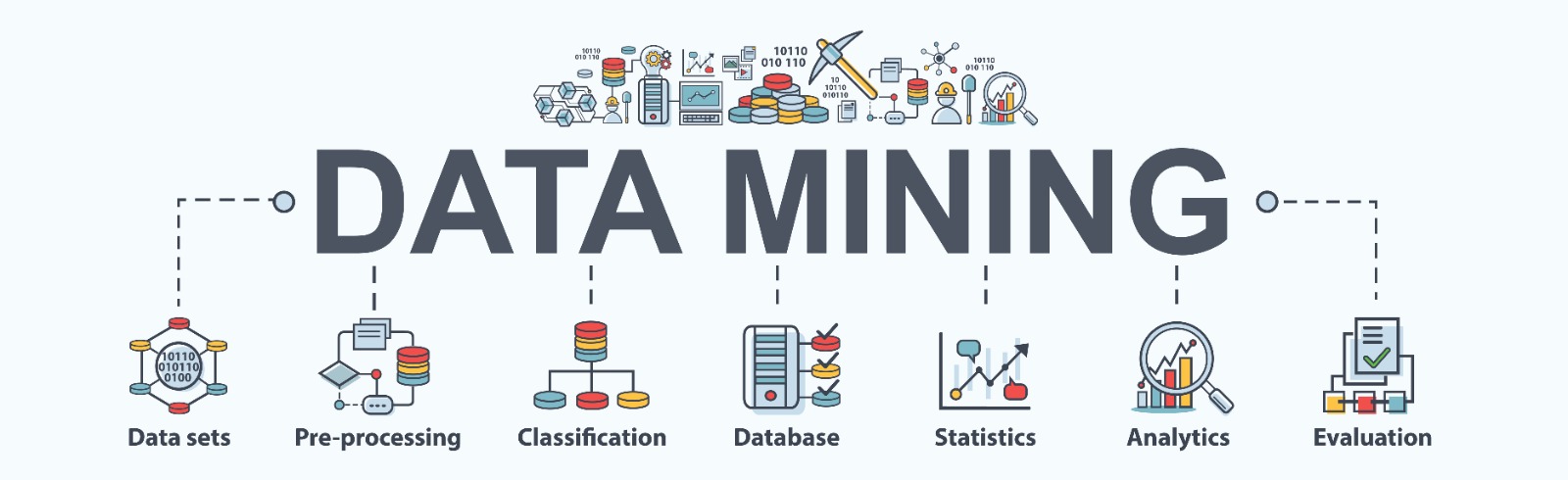
Data skills, including data science and data analytics, are essential for professionals in a variety of fields, including business, healthcare, and education. These skills allow individuals to make informed decisions based on data and to use data to drive improvements in their work. Understanding and applying concepts related to data can have a significant impact on the way professionals approach their work and can help them to be more effective and efficient in their roles.
Needed for Machine Learning Technology to Thrive
Machine learning is a popular application of data analysis that allows companies like Meta and Google to understand and predict the behavior of their users. It involves the use of algorithms to analyze data and make recommendations or predictions. For example, machine learning is used in Google Search to understand the user’s search queries and in social media platforms to recommend products and notifications on news feeds.
The role of a data scientist is to build data models that can help businesses understand and predict human behavior. They use machine learning and statistical modeling techniques to identify patterns and relationships in data. They also design systems for collecting and storing data and apply algorithms to automate processes. Data science and data analytics both involve the use of data to gain insights and improve performance for organizations. While data science focuses on the development of models and algorithms, data analytics focuses on the analysis and interpretation of data to inform decision-making.
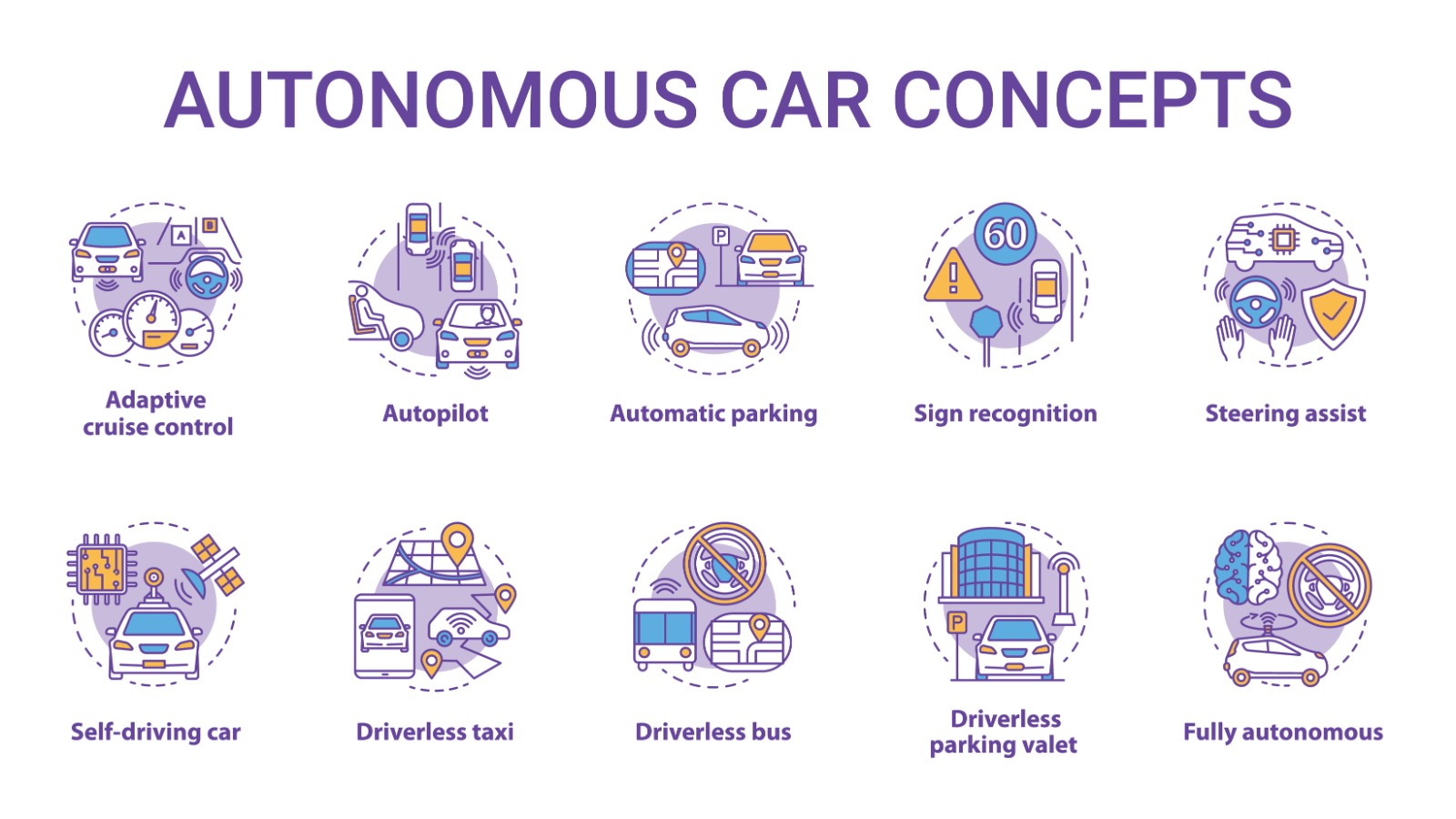
Provides the Future for Advanced Driver Assistance Systems
The volume of autonomous driving (AD) testing has increased significantly in recent years, leading automotive companies to make investments in data processing and analytics professionals in order to advance their ADAS systems. However, collecting and managing data for AD and ADAS development can still be challenging due to the high demand for data and the limited availability of it. Data for AD and ADAS development comes from a variety of sources:
- Raw data: The data that is recorded by on-board sensor systems.
- Derived data: Processing raw sensor data, which results to data subsets.
- Ground-truth data: Used to verify AD functions, human involvement is present to ensure data is provided with high confidence and correctness.
- Metadata: Raw meta information
- Synthetic data: Driving scenarios generated by complex simulators
Effective data management is crucial for the success of AD and ADAS development, particularly as the volume of data continues to grow. By focusing on data-driven approaches and taking into account the future needs of the environment, companies can overcome these challenges and make significant progress in this field.